GENERATING SETS PARALLELING AND SYNCHRONIZATION SYSTEM
The configuration for parallel operation consists of synchronizing two or more generator sets that are coupled together with the same frequency and voltage. They then operate jointly, supplying power to the same network. In this way, energy can be generated in large quantities, which could never be supplied by a single generator set with the same specifications.
Parallel synchronization also applies to those installations that require a much greater reliability and safety mechanism, since having more than one generator operating at the same time is more complicated to fail or fail in unison, thus ensuring continuity, At least partially, of the electricity supply.
Conditions required for parallel synchronization
Connecting the generators in parallel arbitrarily would possibly cause severe damage and the load may lose power, so that to make the parallel connection of two or more generators the following aspects must be taken into account:
- Capacity: easy of synchronizing the system based on load demand; powering on a set when demand increases and switching off a set when demand decreases.
- Redundancy: ensuring a soft power transfer as the outgoing generator is switched off and the incoming one is powered on. The design should avoid a situation where the load is not powered or allowed to run on the UPS.
- Compliance with the electrical standards in terms of safely, protection and operation.
Video:
Why do you need a genset parallel system?
- Maintenance is more convenient. Multiple units are used in parallel, which can be centralized scheduling, distribution of active load and reactive load, maintenance and repair are convenient and timely.
- More economical. According to the size of the online load, a small number of small power gensets can be put in order to reduce the fuel and oil waste caused by the small load operation of the high power generating sets.
- Future expansion is more flexible. It is only necessary to install the power and parallel equipment of the current power required. When the company needs to expand the power grid capacity in the future, the generator set will be added, and can easily realize the parallel of the expansion unit, making the initial investment more economical.
Requirements for connecting generators in parallel
The things to consider are;
- Speed control: The generators may have equal or different engine speeds, but must be locked into the final speed of the system.
- Load balance: The entire load should be shared by all the generators according to the capacity of the individual units.
- Synchronization: Synchronization is required to ensure that the resulting output is in phase, has the same frequency and voltage hence compatible with load.
- Voltage regulation
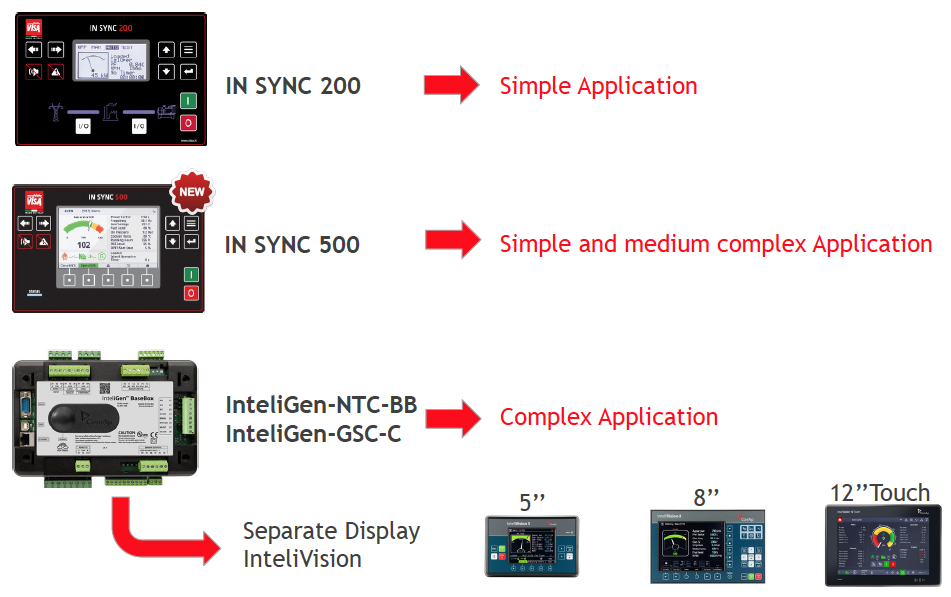
STANDARD Parallel controllers used on Visa Gensets
Gen to Gen parallel & Gen to Mains parallel controller
Examples of typical application:
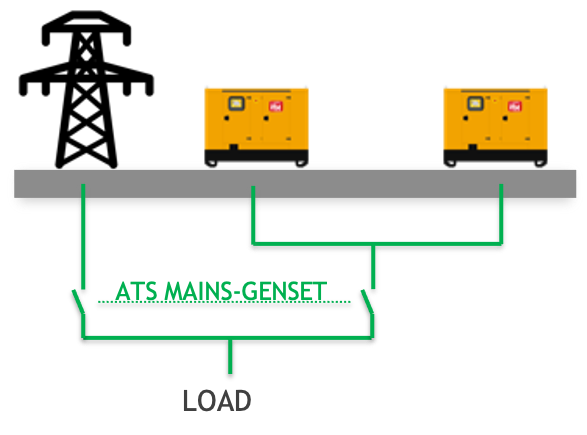
DUAL AMF: 2 redundant GENSETS in emergency to the mains
2 redundant GENSETS in emergency to the mains
- Fixed or variable priority based on hours worked
- Switching between gensets with interruption (absence 1 second)
- During the mains failure, in case of any anomaly occurring to the master genset, the slave unit starts automatically, with an absence of approx 15 seconds.
- 3-way ATS or 2 units of ATS in cascade required
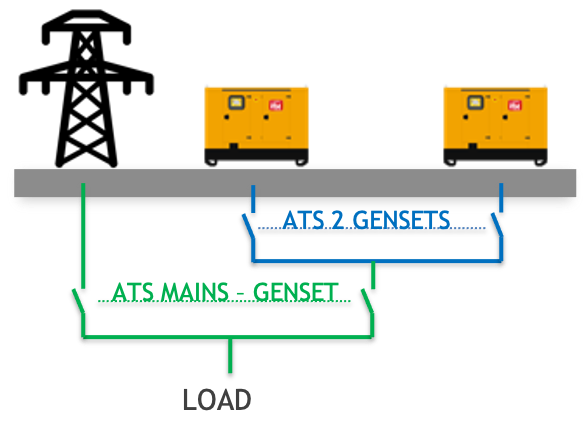
2 redundant GENSETS in parallel, in emergency to the mains
- Possibility to have an active or passive redundancy
- Fixed or variable priority depending on the hours worked
- Switching between GENSETS without interrupmption
- Passive redundancy: during the mains failure, in case of any anomaly occurring to the master genset, the slave unit starts automatically with an absence of approx 15 seconds.
- Active redundancy: during the mains failure, 2 GENSETS are always working; in case of any anomaly occurring to one genset. the other one takes the load without causing any interruption